SwiftUI: Custom Modal (Half Sheet)
Issue
Current SwiftUI offers .sheet() for modal presentation, but there is no control over the look and feel. Moreover there is no native half sheet (as is seen for example in safari) implementation. To our misfortune this design is quite popular between designers. So you have two options, convince your designer it's not a good idea, or shut up and implement it.
Solution
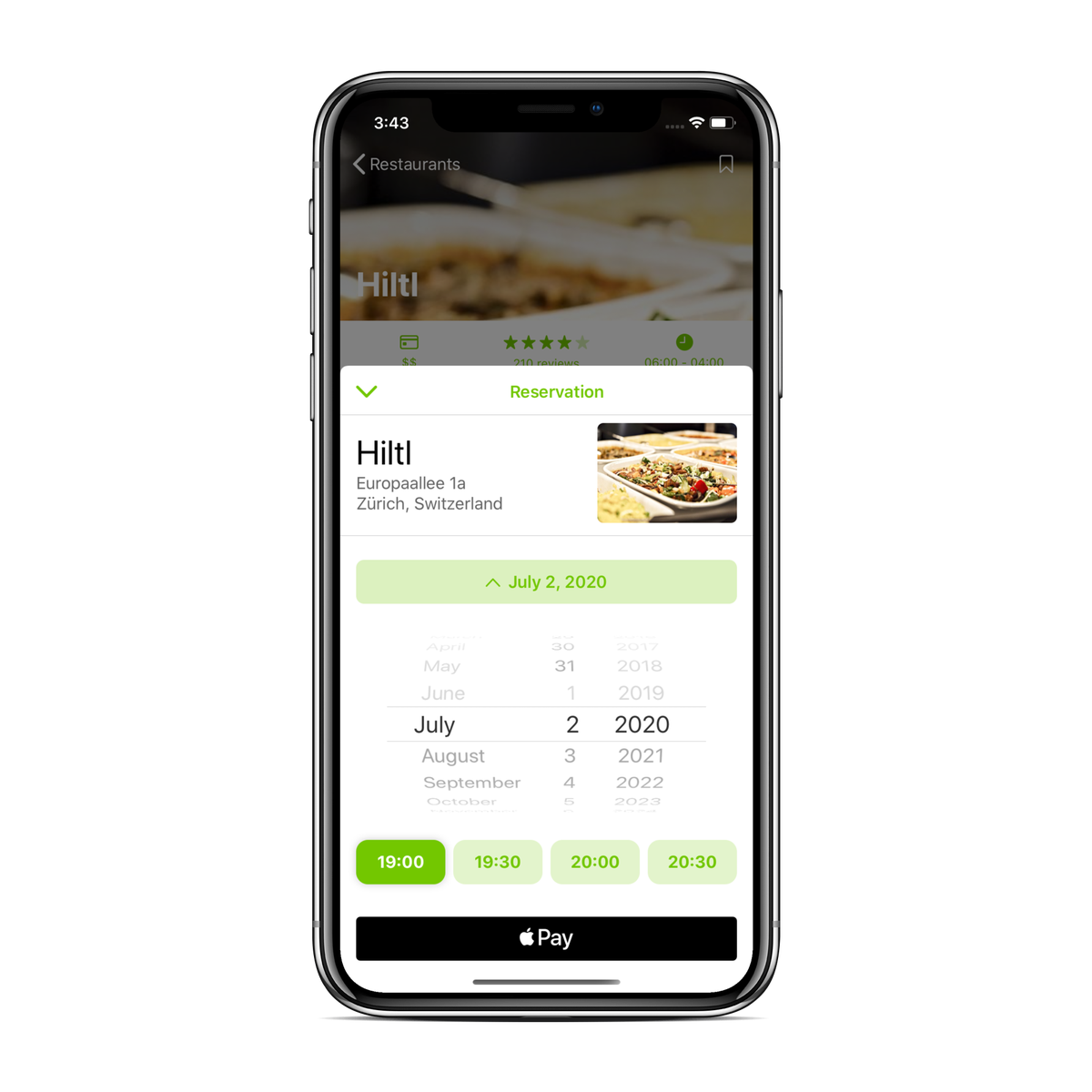
This is the final result (screenshot from my UI kit). And how it can be used in the code.
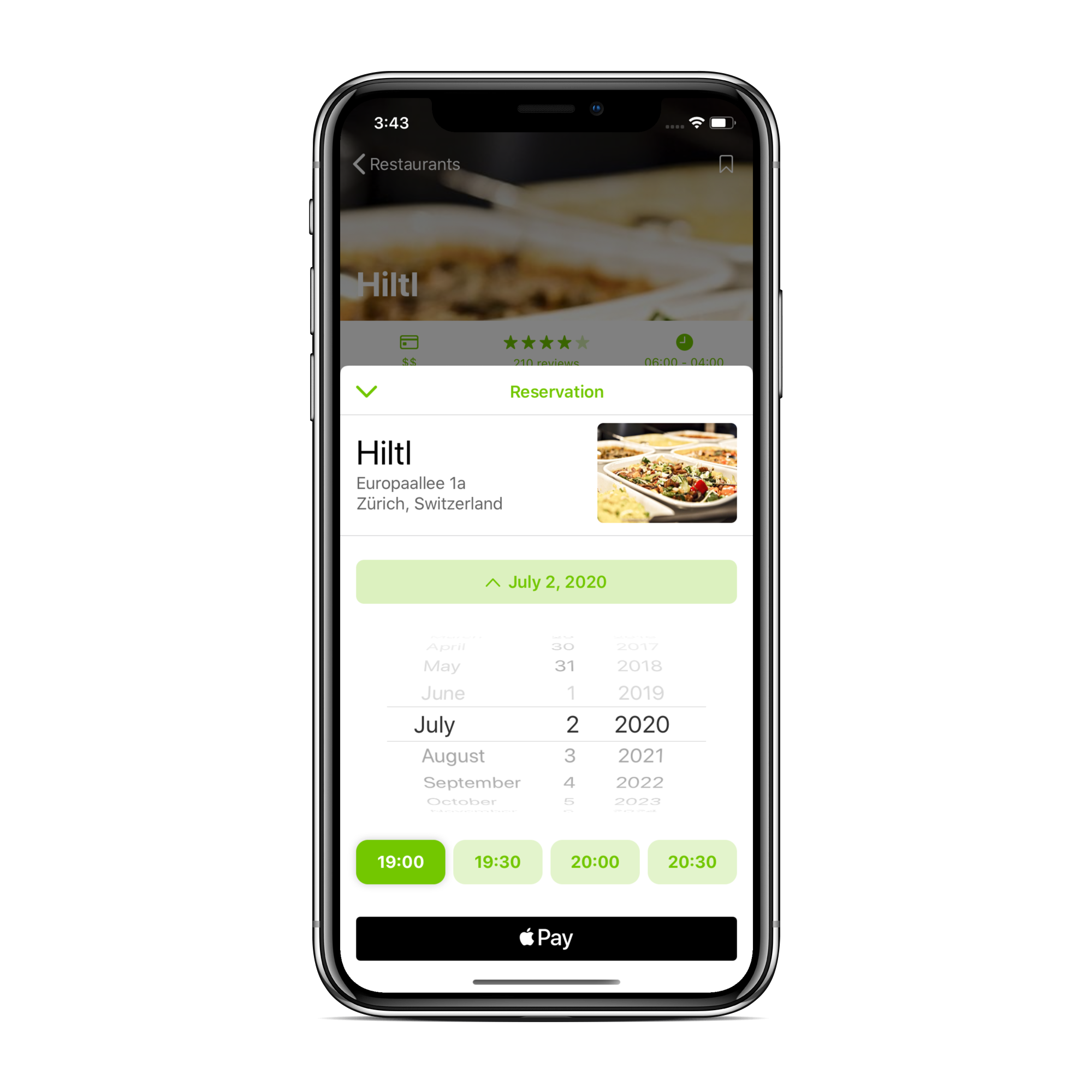
And here is how it's used. First of all you have to create anchor point, from where the modal will be launched.
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
return ZStack {
AnotherView()
ModalAnchorView() // <---- This is the anchor point for the modal
}
}
}And then you can initialized from any of your views as is below:
import SwiftUI
struct SomeView: View {
@EnvironmentObject var modalManager: ModalManager
var body: some View {
return VStack(){
Button(action: self.modalManager.openModal) {
Text("Open Modal")
}
}
.onAppear {
self.modalManager.newModal(position: .closed) {
Text("Modal Content")
}
}
}
}Implementation
We are going to create Modal.swift (model), the AnchorView.swift, ModalManager.swift and ModalView.swift. Let's start with the model. This implementation is inspired by cyrilzakka/SwiftUIModal.
import SwiftUI
enum ModalState: CGFloat {
case closed ,partiallyRevealed, open
func offsetFromTop() -> CGFloat {
switch self {
case .closed:
return UIScreen.main.bounds.height
case .partiallyRevealed:
return UIScreen.main.bounds.height * 1/4
case .open:
return 0
}
}
}
struct Modal {
var position: ModalState = .closed
var dragOffset: CGSize = .zero
var content: AnyView?
}Now let's create the anchor view.
import SwiftUI
struct ModalAnchorView: View {
@EnvironmentObject var modalManager: ModalManager
var body: some View {
ModalView(modal: $modalManager.modal)
}
}Now we can implement our ModalManager, that will handle when to show or hide our modal.
import SwiftUI
class ModalManager: ObservableObject {
@Published var modal: Modal = Modal(position: .closed, content: nil)
func newModal<Content: View>(position: ModalState, @ViewBuilder content: () -> Content ) {
modal = Modal(position: position, content: AnyView(content()))
}
func openModal() {
modal.position = .partiallyRevealed
}
func closeModal() {
modal.position = .closed
}
}And finally the ModalView. This one seems little bit longer, but most of it's implementation is in the method onDragEnded(), that is used for determining where to snap the sheet.
import SwiftUI
struct ModalView: View {
// Modal State
@Binding var modal: Modal
@GestureState var dragState: DragState = .inactive
var animation: Animation {
Animation
.interpolatingSpring(stiffness: 300.0, damping: 30.0, initialVelocity: 10.0)
.delay(0)
}
var body: some View {
let drag = DragGesture(minimumDistance: 30)
.updating($dragState) { drag, state, transaction in
state = .dragging(translation: drag.translation)
}
.onChanged {
self.modal.dragOffset = $0.translation
}
.onEnded(onDragEnded)
return GeometryReader(){ geometry in
ZStack(alignment: .top) {
Color.black
.opacity(self.modal.position != .closed ? 0.5 : 0)
.onTapGesture {
self.modal.position = .closed
}
ZStack(alignment: .top) {
Color("Default")
self.modal.content
.frame(height: UIScreen.main.bounds.height - (self.modal.position.offsetFromTop() + geometry.safeAreaInsets.top + self.dragState.translation.height))
}
.mask(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 8, style: .continuous))
.offset(y: max(0, self.modal.position.offsetFromTop() + self.dragState.translation.height + geometry.safeAreaInsets.top))
.gesture(drag)
.animation(self.dragState.isDragging ? nil : self.animation)
}
}
.edgesIgnoringSafeArea(.top)
}
private func onDragEnded(drag: DragGesture.Value) {
// Setting stops
let higherStop: ModalState
let lowerStop: ModalState
// Nearest position for drawer to snap to.
let nearestPosition: ModalState
// Determining the direction of the drag gesture and its distance from the top
let dragDirection = drag.predictedEndLocation.y - drag.location.y
let offsetFromTopOfView = modal.position.offsetFromTop() + drag.translation.height
// Determining whether drawer is above or below `.partiallyRevealed` threshold for snapping behavior.
if offsetFromTopOfView <= ModalState.partiallyRevealed.offsetFromTop() {
higherStop = .open
lowerStop = .partiallyRevealed
} else {
higherStop = .partiallyRevealed
lowerStop = .closed
}
// Determining whether drawer is closest to top or bottom
if (offsetFromTopOfView - higherStop.offsetFromTop()) < (lowerStop.offsetFromTop() - offsetFromTopOfView) {
nearestPosition = higherStop
} else {
nearestPosition = lowerStop
}
// Determining the drawer's position.
if dragDirection > 0 {
modal.position = lowerStop
} else if dragDirection < 0 {
modal.position = higherStop
} else {
modal.position = nearestPosition
}
}
}
enum DragState {
case inactive
case dragging(translation: CGSize)
var translation: CGSize {
switch self {
case .inactive:
return .zero
case .dragging(let translation):
return translation
}
}
var isDragging: Bool {
switch self {
case .inactive:
return false
case .dragging:
return true
}
}
}SwiftUI Elements
You can find also the whole implementation in my open source UI kit